Choosing Cost-Effective 100G Transceivers for Data Centers
As the deployment of services like AI, deep learning, and big data analytics scales up, data center networks are advancing towards 100G and even higher speed rates.
The construction of a 100G network necessitates a significant number of 100G optical modules, which account for a high proportion of the total construction costs.
Selecting cost-effective 100G optical modules is crucial for budget management and overall efficiency.
This article introduces essential knowledge about 100G optical modules and guides you in choosing the most cost-effective options for your needs.
Types of 100G Optical Modules
The market currently offers several types of 100G optical modules: CXP, CFP, CFP2, CFP4, and QSFP28 modules.
CXP Modules
CXP modules offer high transmission rates of up to 12×10Gbps and support hot-swapping. They are primarily aimed at the high-speed computing market and supplement CFP modules in Ethernet data centers, with applications in short-distance data transmission when paired with multimode fiber.
CFP/CFP2/CFP4 Modules
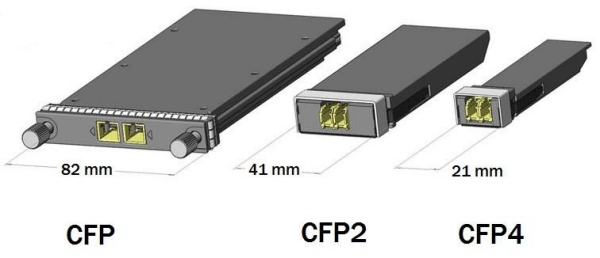
CFP modules were designed based on the small form-factor pluggable (SFP) interface and support 100 Gbps data transmission. They support a variety of rates, protocols, and link lengths over single-mode and multimode fibers, including all physical medium dependent (PMD) interfaces contained in the IEEE 802.3ba standard.
The large size of CFP modules, however, has led to the development of CFP2 and CFP4 modules to meet the high-density requirements of modern data centers.
QSFP28 Modules
The Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus 28 (QSFP28) module is increasingly popular due to its small size and four channels, each with a maximum rate of 28Gbps.
QSFP28 modules offer a higher density advantage over CFP4 modules, although CFP4's higher maximum power consumption gives it an edge in longer-distance optical transmission.
Applications of 100G Optical Modules
Short-Distance Transmission
For short-distance transmission, the standards mainly include 100GBASE-SR10 and 100GBASE-SR4.
The 100GBASE-SR4 standard emerged as the electrical interface rates of switch ASIC chips increased from 10Gbps to 25Gbps,
transitioning from CAUI-10 to CAUI-4. This shift has resulted in smaller, less costly, and lower power consumption 100G modules.
Medium-Distance Transmission
Medium-distance transmission standards mainly include 100GBASE-PSM4 and 100GBASE-LR4,
with transmission distances within 500M for PSM4 and up to 10KM for LR4. Prominent modules for these standards are the 100G QSFP28 PSM4 and 100G QSFP28 LR4 modules.
Long-Distance Transmission
For long-distance transmission, the standard is mainly 100GBASE-ER4, with a maximum transmission distance of up to 40km. This is typically used in data center intra-networks, data center interconnects, and metropolitan area networks.
Packaging of 100G Optical Modules
The packaging formats for 100G optical modules include CFP, CFP2, CFP4, and QSFP28, with QSFP28 being the most popular.
The CFP was the earliest packaging for 100G modules, but it has been largely phased out due to its size. As the integration of optical modules has increased, the industry has seen a progression from CFP to CFP2, CFP4, and eventually to QSFP28, with continuous reductions in module size and power consumption.
When you are choosing 100G optical modules, consider not only the type and packaging but also the specific application, distance requirements and power consumption.
Ensure that you select the most cost-effective solution for your data center's needs.
If you need any products or Data Center Solution, contact us!

