Basic Guide of Data Center
A data center is a physical facility that houses IT infrastructure for building, running, and delivering applications and services, and for storing and managing the data associated with those applications and services.
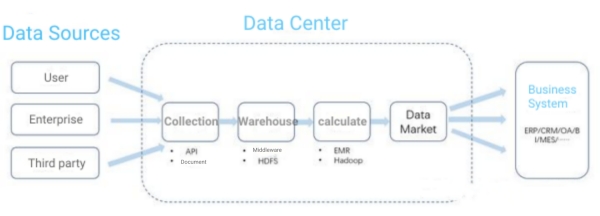
How a Data Center Works
A simple data center operates to maximize the efficiency of data processing (computation and storage).
However, achieving such efficiency often means an increase in the cost of building the data center.
Therefore, the construction of a data center should meet business needs (short-term and long-term) and control costs as much as possible.
In recent years, as data gradually become a company's core assets, data security has become a key issue for companies and even countries. Therefore, in selecting equipment for data centers, both functionality and cost need to be considered. Basic considerations include:
- Network reliability and security
- Data volume (business scale, collection frequency)
- Data computation frequency (t+0, t+1)
- Security requirements (such as security audits)
- Others
Based on these considerations, companies will design their data center infrastructure according to their business needs.
For example, a multinational manufacturing company will naturally have higher requirements for network, computation, and security than a small and medium-sized enterprise.
IT Equipment in Data Centers
Typical IT equipment in data centers includes:
-
Network: The role of the network is to facilitate interconnection between devices within the data center and external connectivity. The product composition includes network lines (public and dedicated), network devices (selected according to actual business needs). Data centers often use Top of Rack (TOR) switches responsible for networking within the rack and connecting to upper layer switches. Performance indicators include packet loss rate and delay jitter.
-
Servers: The primary purpose of servers is computation, and computation needs vary based on business requirements. For example, load balancing, message middleware, big data applications deployed in data centers, SAAS systems, etc., are all directly configured on servers. Performance indicators include CPU, memory, and disk.
-
Storage: The role of storage is for data storage and read/write operations. As most companies (especially large companies today) have a large amount of data, the cash cost for storage is not low. Therefore, companies will choose different storage products according to actual business needs to ensure business while controlling costs. Performance indicators include read/write speed, stability (fault response), and compression rate. Product categories include common storage service types DAS, NAS, SAN; traditional physical storage categories include block storage, file storage, object storage, table storage.
-
Security: The role of security products is to protect data assets. Depending on the data flow path, user-data interaction method, security products will be divided into network request-based security products (firewalls, WAF, etc.), traffic-based data asset security products, and operation-based (terminal) security products. Depending on the characteristics of the security products, different machines will be needed. For example, firewalls are typically network devices, while WAF and data security products are implemented through servers. Network request-based security products include firewalls, WAF, IPS, anti-DDOS, CC. Data asset-based security products include database security. Terminal behavior-based security includes bastion host, terminal virtual desktop.
Development of IT Technology Related to Data Centers
-
Hardware: Network cables are being replaced by optical fibers to improve network transmission speed. Smart network card technology is being used to perform protocol processing itself, relieve CPU pressure, and improve throughput. The CPU has evolved to GPU, and now to AI professional chips to increase computing power. Storage has evolved from HDD to SDD, and now to SCM (Storage Class Memory). The future trend is SCM+AI/ML.
-
Software: Load balancing is a software solution for balancing network server bandwidth. VPN is a virtual private network that virtualizes a dedicated channel in the same physical space to ensure communication isolation and confidentiality.
Edge computing relies on edge servers deployed everywhere to perform some instant service computations to improve response speed.
CDN uses the concept of edge computing, caching content in advance to edge servers so that users can obtain required content nearby, improving user access response speed.
SDWAN is a path optimization software solution based on the transmission protocol. There is no need to adjust the original physical equipment.
Distributed technology is widely used in storage and computation, distributed computation, distributed storage, distributed databases, etc.
If you need data center products and solutions, the professional team at fibeye is here to serve you!

